Pandas
Pandas has two built-in data types: series and data frame - Series are columns in the dataset - Data Frame is the object the dataset to a data type that can be use in pandas
Function:
Initial data exploration:
df = pd.read_csv("path_to_dataset"): load datasetdf.info(): what types are useddf.describe(): overview of the numerical data, gives the most important statistical analysis.df[column].isna(): by checking which values are NaN, with True and False values.df.dropna(axis, how, subset, thresh): drop rows if any values is NaNdf.fillna(value, method, axis, limit): replace NA with mean, max or min values of the column, strings and 0.df.nunique(): how many unique values we have in each column of the Dataframe.df.duplicated(): To search for entire rows of data that duplicate other rows, and return a maskpd.to_numeric(df[column], error={'ignore','raise','coerce'}, downcast={'integer','signed','unsigned','float'}): ensure every entry in a column is numeric.df.groupby("series"): Splitting dataframe bu categorical value inside this series
Explore information of one column
pd.unique(column): Return unique values based on hash table.Series.value_counts(): Return a Series containing counts of unique valuesSeries.mean(): Return the mean of the values over the requested axisSeries.size(): Return the number of elements in the underlying data
Data manipulation
pd.concat(df, axis, join):append one data structures to the other along one axispd.merge(dataframe1. dataframe2. on, how): Merge two dataframes by one or multiple Keys/ Indices, A little bit like Join in SQL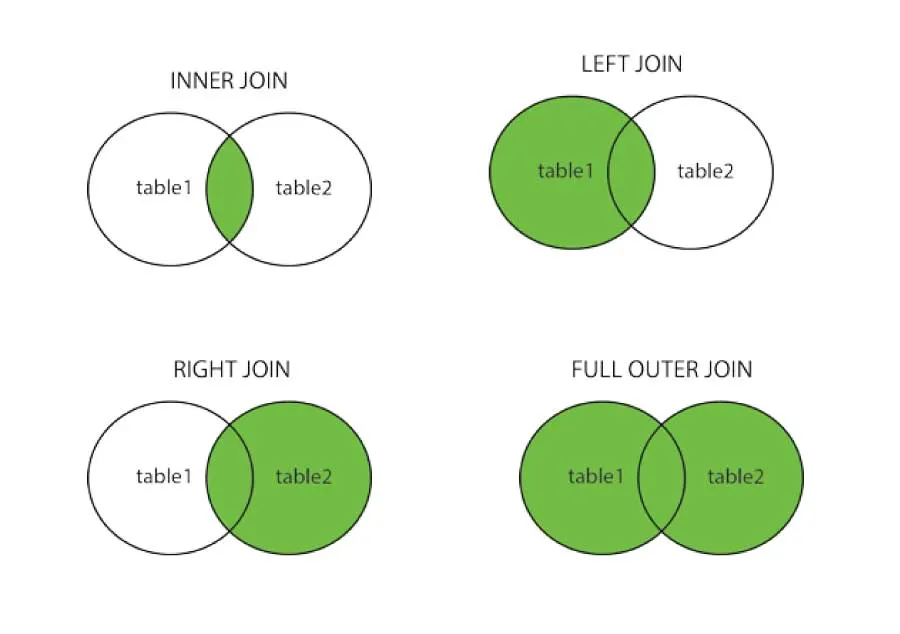
df_filtered = df[df["Column"].isin([specific value1, specific value2])]: Filter rows that contain specifc values in a column:.df.drop('column name', axis=1): Remove column or columns- axis=1: Column operations
DataFrame.reset_index: Change multiIndex back to a regular column and reset it to the default numeric index.Series.apply(): Invoke function on values of Seriespd.DataFrame(data={'col1':[1,2], 'col2':[3,4]}): create dataframe
Date
Series.dt.to_period(freq): Covert DatetimeArray to PeriodArray- freq: W, M, Q, Y
Fact:
- type(np.NaN) = float, which means coerce a column can apply all numeric operations to entire columns.
- mask is a series return True and False
- ~ will revert boolean values in a series