In this semester, I listened the course mit 6.006 in youtube channel. Duirng the course, the professor used different notations to represents time complexity of an algorithm. I learned Big O O(n) notation before, but for Big theta θ(n) and reccurence relations T(n), I never heard them before. Today, I hope I can finally figure them out.
What
T(n) represents the actual running time of an algorithm
O(n) represents the asymptotic upper bound of the running time of an algorithm
θ(n) represents the running time when asymptotic upper bound and lower bound of an algorithm ares the same.
How to convert the three of them
- Normally we can directly transfer T(n) to O(n) or θ(n).
Int sum = 0
for (i = 1; i <= n, i ++) {
sum = sum + i
}
This is a classical example,
First of all, we initialize variable sum requires one unit of running time. There are three statements inside the for loop, statement 1 i = 1 requires one unit of the running time, statement 2 i <= n requires n+1 units of the running time,
statement 3 i ++ requires n units of the runningn time,
and sum = sum + i requires 2n units of the running time, n for addition and n for assignment. Therefore T(n) = 1+1+(n+1)+n+2n = 4n + 3. In O(n), we ignore the constant and the lower-order terms, therefore the time complexity is O(n) / θ(n).
When the algorithm is a recursion, such as karatsuba multiplication and high precision multiplication.
 There are two methods to convert T(n) into O(n)
There are two methods to convert T(n) into O(n)
- Recursion tree method
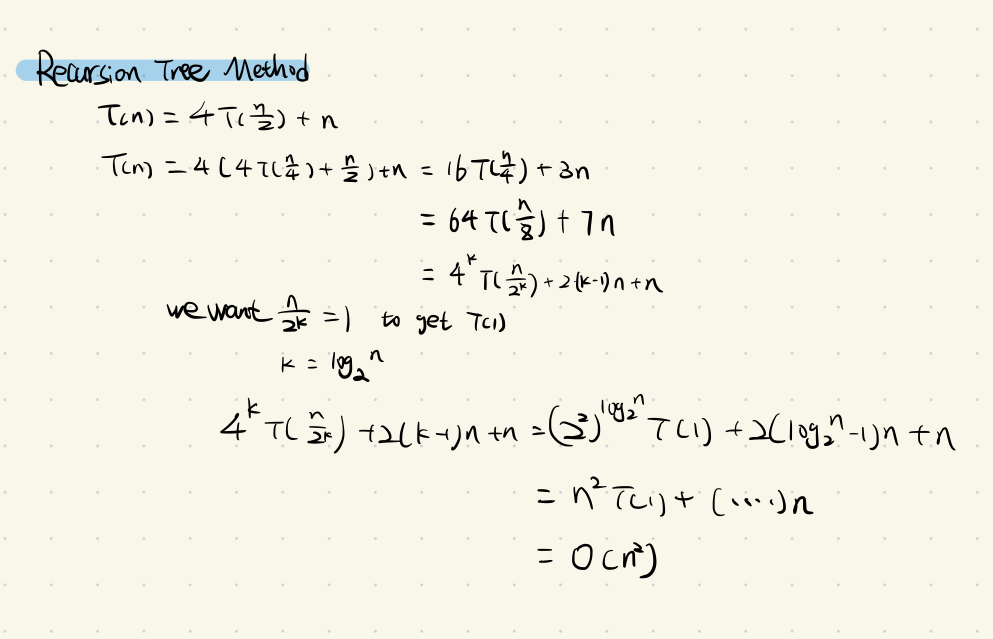
- According to Recursion tree method, we derive master theorem

The time complexity of multiplication is equal to the time complexity of division