Bitcoin
The legend of Bitcoin has shown its magic for a long time. Recently, I have started to explore this field, and this is a record of my learning.
The Blockchain⛓️
The blockchain is the foundational technology of Bitcoin. Think of it as a public, digital ledger or receipt book that is shared across thousands of computers worldwide.
- It’s a Chain of Blocks: Each “block” contains a list of recent transactions. When a new block is created, it is cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming an unbroken chain leading all the way back to the very first block.
- It’s Immutable: Because each block is linked to the one before it, changing a transaction in an old block would require re-doing all the work for every single block that came after it. This makes the ledger permanent and tamper-proof. This structure is what proves each coin’s history and prevents fraud like double-spending.
The Genesis Block📜
The very first block, known as the Genesis Block, was mined on 2009.01.04, by Bitcoin’s mysterious creator, Satoshi Nakamoto. This single block was the start of the entire Bitcoin network. Once it was created, the race to mine the second block began, and the chain has been growing continuously ever since.
Mining⛏️
Mining is the process of creating new blocks. It’s a competitive race that serves two critical purposes:
- Validating Transactions: Miners group pending transactions into a new block.
- Creating New Bitcoin: The winner of the race is rewarded with new bitcoin.
Here’s how a miner wins the race and proves their block is valid:
- The Hashing Puzzle: Miners take the data in their block and use their computers to find a specific number called a nonce. When the block data and the nonce are combined and put through a cryptographic function (SHA-256), they produce a unique digital fingerprint called a hash.
- The “Lower Than” Rule: To win, a miner must find a hash that is lower than the current network “target”. This target is a very large number that the entire network agrees on. Finding a hash below this target is incredibly difficult and requires immense computational power—it’s like trying to win a global lottery every 10 minutes.
- The Reward and The Halving: The first miner to find a valid hash wins the block reward.
- Initially, the reward was 50 BTC.
- However, this reward is programmed to cut in half roughly every four years (or 210,000 blocks) in an event called the halving.
- As of the April 2024 halving, the reward is now 3.125 BTC.
- This mechanism controls the supply of new bitcoin, making the currency scarce and ensuring its total amount will never exceed 21 million coins.
When a winning block is found, its hash is broadcast across the P2P network. All other participants quickly verify that the hash is valid. Once confirmed, they add the new block to their copy of the blockchain and immediately start competing to solve the next block.
How to Mine:
There are a few ways to participate in Bitcoin mining, each with its own pros and cons.
- Solo Mining: This is you, on your own, trying to solve a block. If you succeed, you get the entire block reward (3.125 BTC + transaction fees). However, the odds of a single person solving a block today are astronomically low due to the immense competition. It’s like buying a single lottery ticket and hoping to win the grand prize.
- Mining Pool: This is the most common method. You join a “pool” with thousands of other miners, combining your computing power. The pool works together to find blocks much more frequently. When the pool wins, the reward is split among all participants based on how much computing power they contributed. This provides smaller, but much more consistent and predictable, payouts.
Block Forks🍴
A fork happens when the blockchain temporarily or permanently splits into two different paths.
- Accidental Fork: Sometimes, two miners find a valid block at almost the exact same time. The network briefly splits as some nodes follow one miner and some follow the other. This is usually resolved within a few minutes when the next block is found and added to one of the chains, making it the “longest” and therefore the official one. The shorter chain is then abandoned.
- Hard Fork: This is an intentional split that happens when the network’s software rules are changed in a way that is not backward-compatible. All participants must upgrade to the new rules to continue. If a significant portion of the community refuses to upgrade, the split becomes permanent, resulting in the creation of a new, separate cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin Cash was created from a hard fork of Bitcoin).
Ethics
Mining bitcoin always consume immense energy, which critics view as a wasteful environmental cost for a seemingly meaningless computation. Proponents argue this mechanism decentralized financial system that offers freedom from the control of banks and governments.
Tools
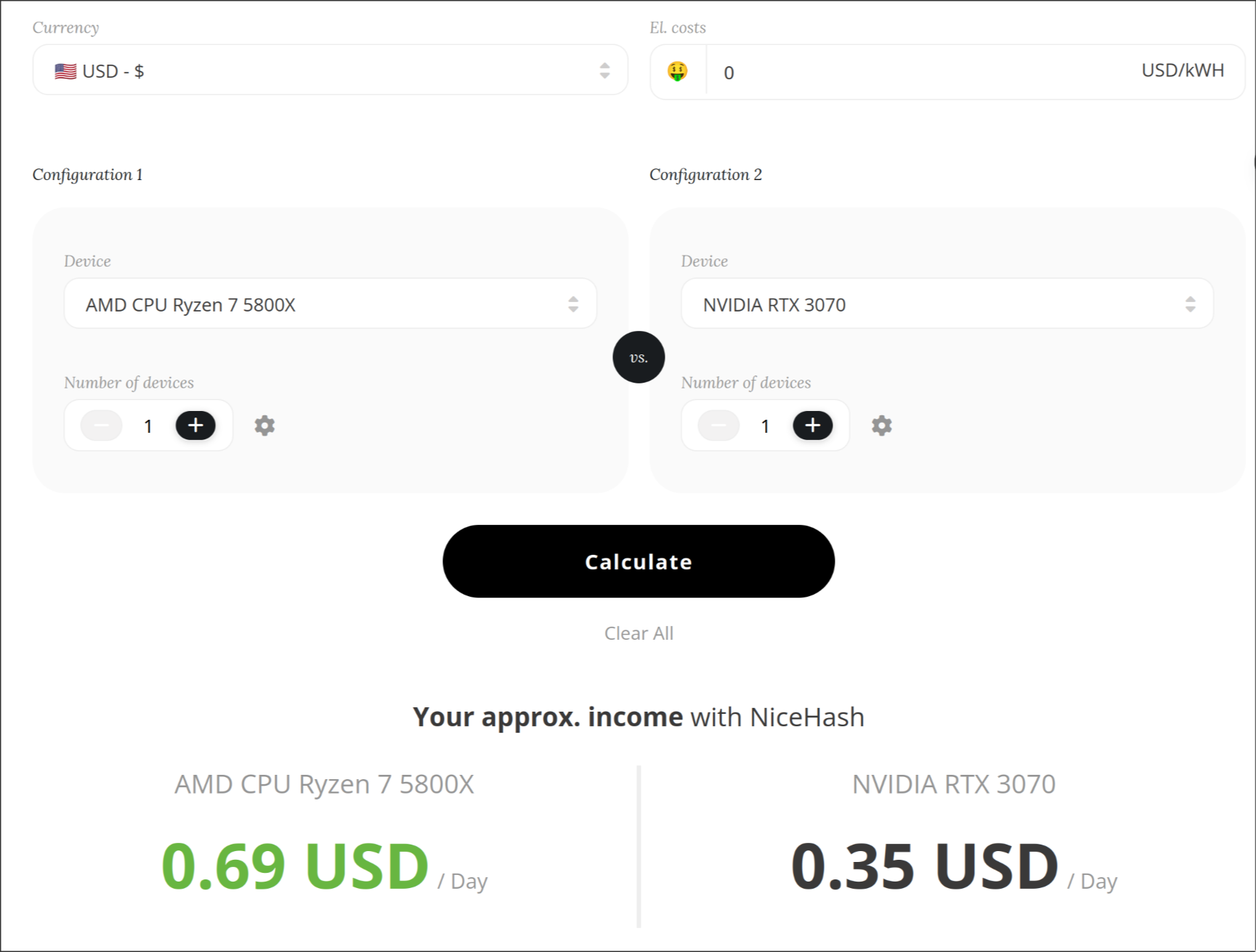
Calculate computing performance: https://www.nicehash.com/profitability-calculator
This is the computating power of my personal game laptop(one dollar per day hhh)
Resources:
Youtube channels
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5hgdekVZb3A&list=PL5TbbtexT8T0JbaWR0Zbf-aVm2onpSjHT&index=3
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a41DMDfJjsU&list=PL5TbbtexT8T0JbaWR0Zbf-aVm2onpSjHT&index=2
- https://Gemini.google.com
Trivias
- Sherrington, coined the word “synapse” to define the connection between two neurons
- Two different roads of AI: connectionism and Symbolism.
- Hidden layer was firstly been implemented in Boltzmann machine, although Rosenblatt had some idea about multilayer perceptrons, but he didn’t find any useful training algorithm.
- Restricted Boltzmann machine - each layer is only allowed to be fully connectted to the next layer, current layer nodes are not connectted to each other. The advantages of this machine is it allows to update bodes within the same layer in parallel
- The invention of hidden layer allows model to understand abstract features. It also becomes to one of the most significant component in deep learning.
- The main difference between the Hopfield Network and the Boltzmann nachine is the presence of hidden layers. Other differences include the fact that the Hopfield network is deterministic, whereas the Boltzmann machine is stochastic, and the defintions of their energy function also differ.
- The fovea has many photoreceptors, with a high density of cones(for colors) and nearly no rods(for dark). This structure allows us to see the world clearly. If you develop myopia, the image formed after light is reflected by the eye may not be focused directly on the fovea.
- The idea of CNN was mainly inspired by the HMAX model(hierarchical, pooling, convolution), and the HMAX model was proposed by Tomaso Poggio, to simulate primate visual system, specifically ventral stream.
- Pytorch for research area, Tensorflow for industry and JAX for high level usage.
- Ethereum and ether is not the same as bitcoin. Ethereum has a longer vision, and the number of ether is unlimited.
Resource
- Documentary of AlphaGo: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WXuK6gekU1Y
- How to use hugging face: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3kRB2TXewus
- This is the most comprehensive guide for AI beginner I had ever seen: Guide link