Model Context Protocol overview
MCP (Model Context Protocol) can be understood as a “universal language” for communication between AI and external tools. It’s like a translator, allowing different AI applications (such as chatbots, code assistants) and different tools (like databases, GitHub, calendars) to easily communicate without needing to develop a new interface every time.
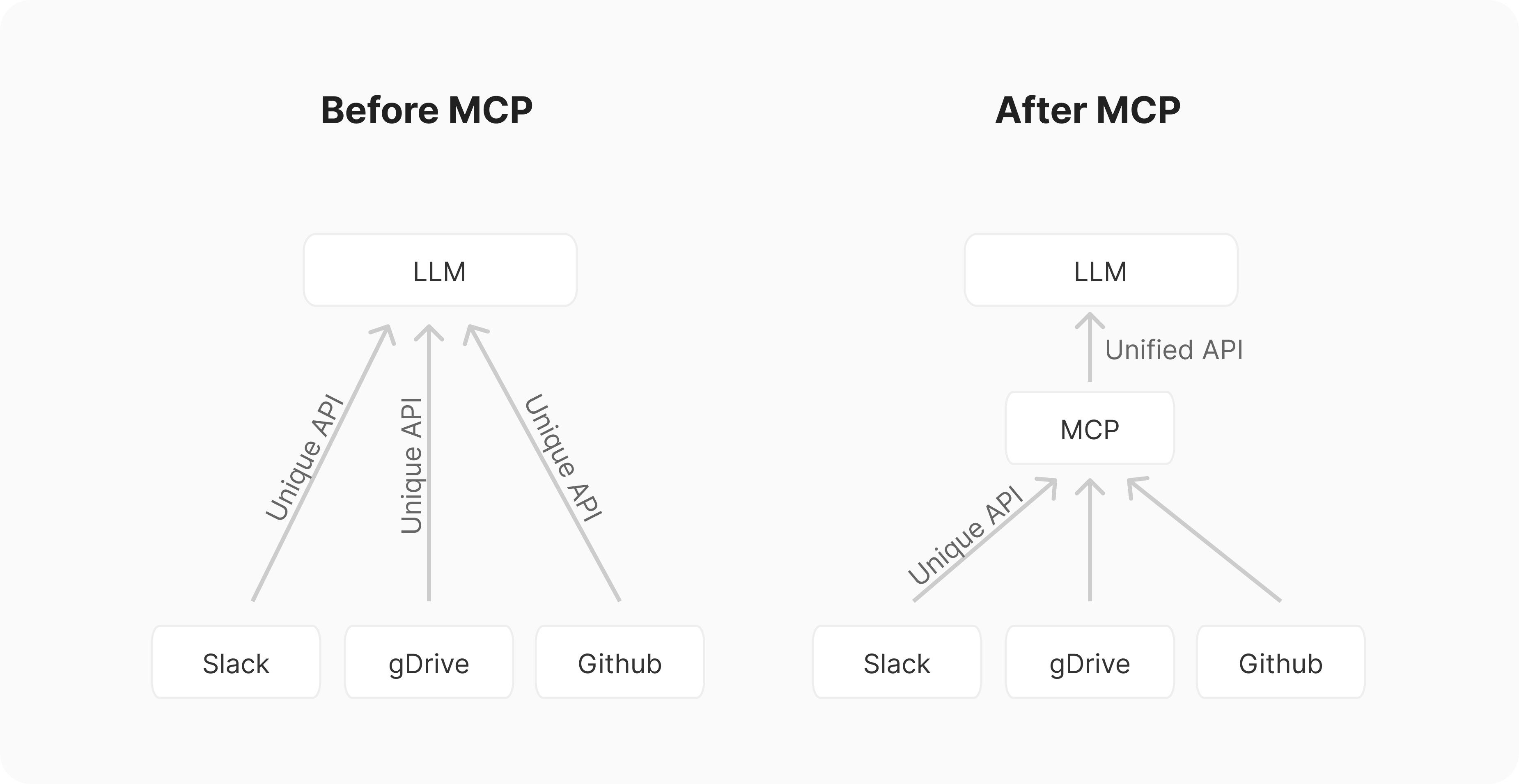
Why is MCP needed?
In the past, if you wanted an AI assistant to access different tools, like a calendar, email, or task manager, you would need to develop a separate interface for each tool (function calling), which resulted in a huge amount of work (N AI applications × M tools = N×M interfaces).
MCP simplifies everything: all AI applications only need to support MCP, and all tools only need to support MCP. This way, they can communicate with each other, reducing development costs (N+M interfaces).
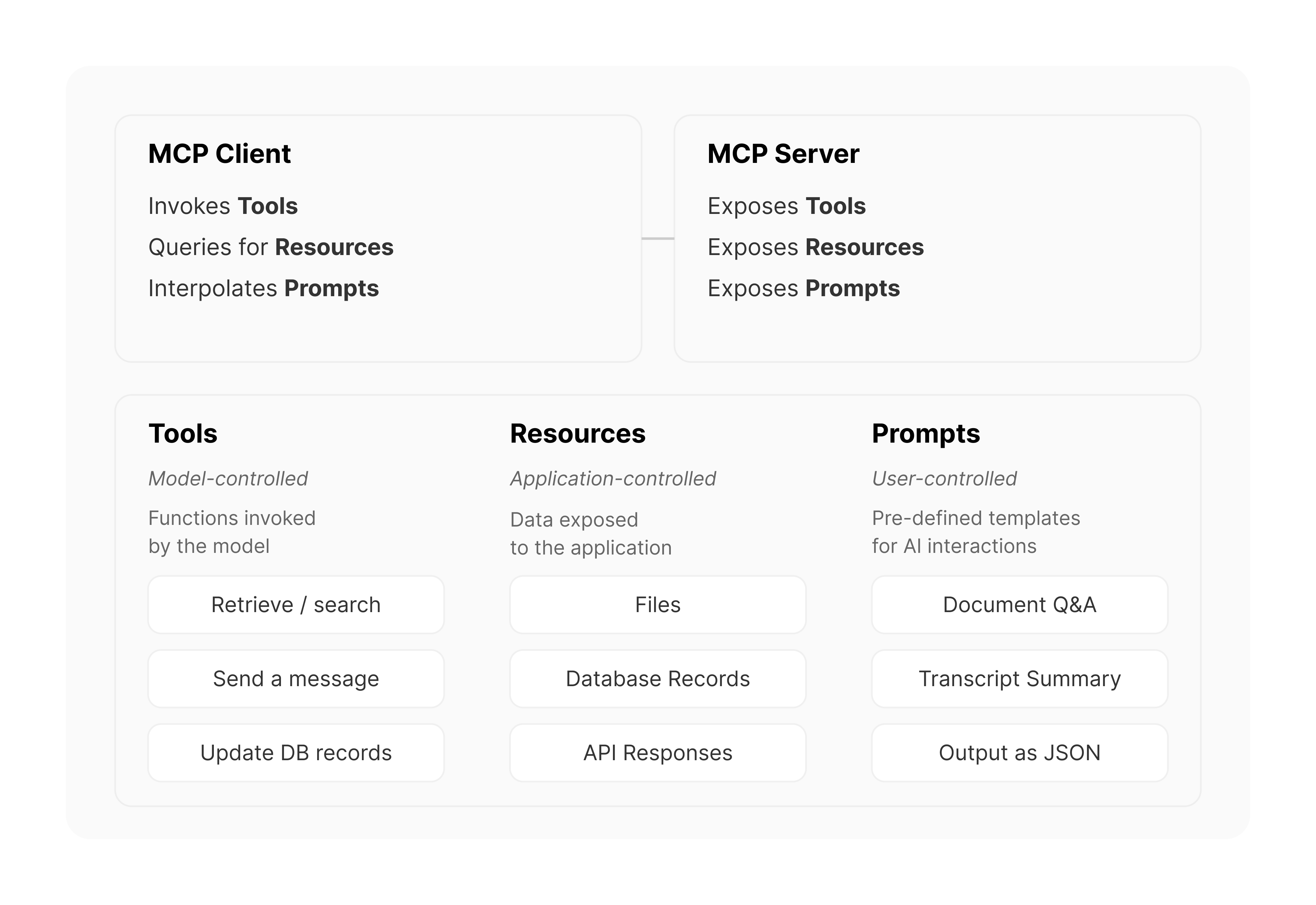
The current components of MCP servers include:
How does MCP work?
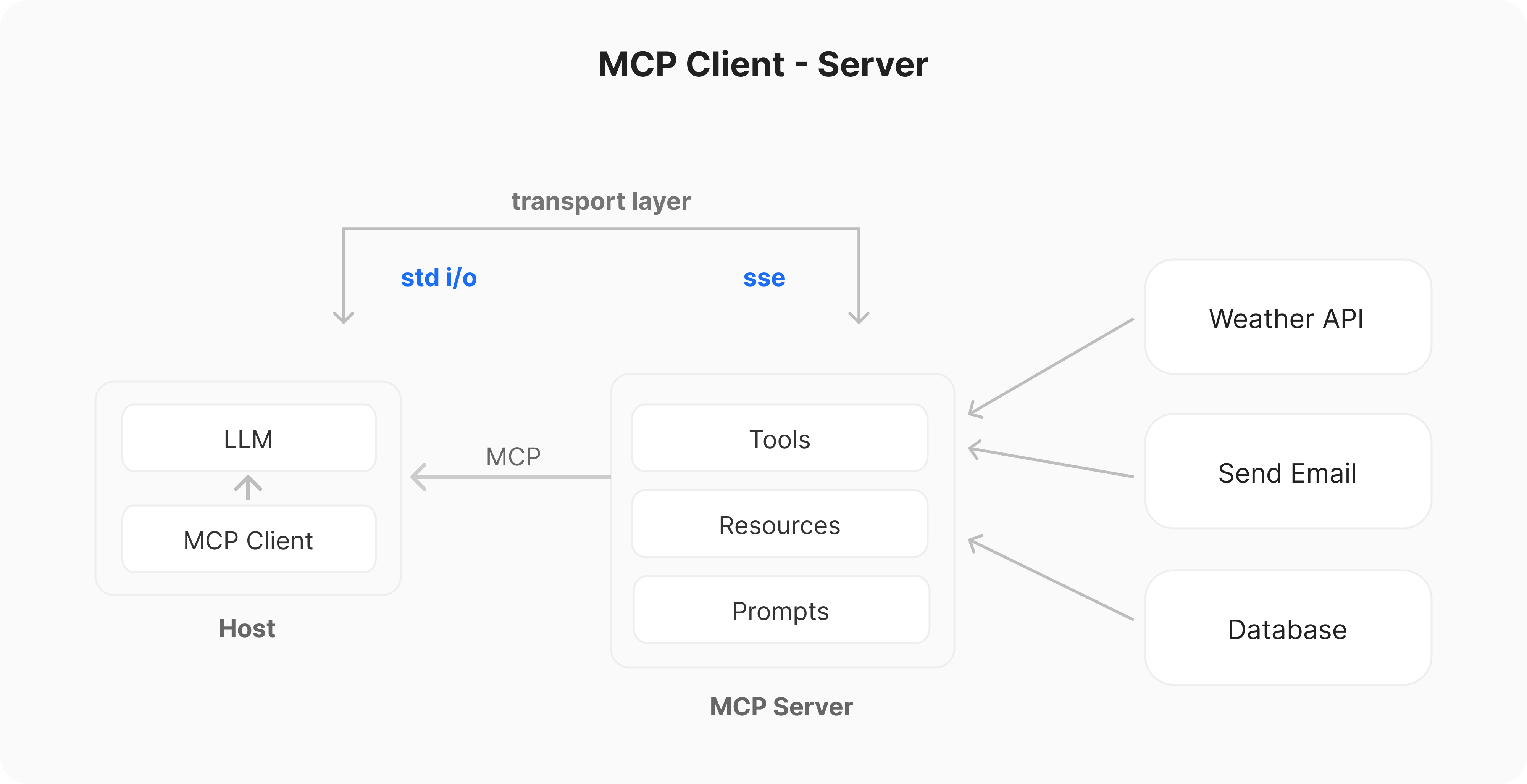
Example:
Suppose you’re using an AI assistant to manage your work, and it wants to help you schedule today’s meeting:
Without MCP, developers would need to write separate integration code for Outlook, Google Calendar, and Apple Calendar.
With MCP, the AI only needs to call the MCP server, which will automatically interface with your calendar system. No matter which calendar service you use, the AI can work seamlessly.
Core Functions of MCP:
Reducing development costs (no need to develop separate integrations for each tool).
Enhancing AI’s ability to access external data (allowing AI to easily query and manipulate external data).
Standardizing communication (making communication between different AI applications and tools smoother).
You can think of MCP as the “USB interface for AI”—any AI device can plug into different tools without needing to individually adapt to each one!
Trivias:
Graphis a great data structure, it can be used to find the shortest path, solve a magic cube. Rely on this data structure, Human find the shortest steps to solve the worst case configured3\*3\*3magic cube in 20 steps (which also called god’s number) and 11 steps for2\*2\*2one. What about n*n*n, Here is an interesing paper about time compleixity of solving a n*n*n magic cube: Algorithms for Solving Rubik’s Cubes- Topological sort is an algorithm based on DFS and DAG, It’s not a traditional sorting algorithm, like comparing the size of each number and sort them, but sorting based on dependencies.
- Dynamic programming is just like recursion + memorization + guessing
- P vs NP problems: P is a problem that can be solved easily by a computer, NP is a problem that you can check for correctness very easily once solved. However, P != NP for example wec can’t engineer luck. Also, NP hard means it is at least as hard as any problem in NP, and NP-complete is lke if you can solve one NP-complete question, you can solve all NP question. Reduction is like to prove a known NP-complete question, and transfer it into a NP question X, then X is also a NP-complete question
- HTTP vs REST API
HTTP is a protocol, and its core task is to define how to request and transfer data between your broswer and server
- It focuses on the data exchange level, regardless of whether the data is an image, text, video, or API response.
- For example, you can use an HTTP request to access a webpage (HTML page) or use an HTTP request to retrieve API data (JSON data). It doesn’t care about what data you’re transmitting.
REST API is a design style, based on the HTTP protocol, with rules and best practices:
- It views content on the server as “resources” and specifies how to operate on them using HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
- REST API design considers resource orientation: Resources (like users, articles, comments, etc.) have unique identifiers (URIs), and clients interact with these resources through HTTP requests.
For example, in a REST API, you can:
- GET request: Retrieve a resource (e.g., get movie information).
- POST request: Create a new resource (e.g., submit a new comment).
- PUT request: Update a resource (e.g., modify user information).
- DELETE request: Delete a resource (e.g., remove an article).
Resource:
- A tool to build a personal streaming music player: navidrome
- A great blog that introduce human visualization: human visualization
- Five basic algorithms explanation:
- This week, Nvidia GTC 2025 brings a lot of new tech, PC in AI age, B300, new architecture, robots.
After watched the coverage keynotes, I was just feel like our mankind is in an special stage with unpredictable pace. In science fiction films, at this point
, it often leads to the arrival of an alien civilization.
- A dijkstra algorithm visualiser that helps me understand it: Dijkstra shortest path
- MCP explain: A blog that explain MCP crystal clear